Despite the fact that 3D printing and injection molding are two widely used processing techniques, their process principles are fundamentally different. These two technologies can assist you in making and producing items more quickly, depending on the requirements of your project. Their respective advantages are numerous, and both of them will be beneficial to your manufacturing process, which is why it is critical to understand the differences between the two approaches. As a result, in this guide, we will examine the differences between 3D printing and injection molding from a variety of perspectives.
What Is Injection Molding and How Does It Work?
Molded products are produced by injection molding, which is a process in which the plastic material is completely melted by screw stirring at a specific temperature, injected into the mold cavity with high pressure, then cooled and solidified to produce the final product. It is generally considered suitable for the mass production of some simple objects with a high level of production efficiency in most situations. This procedure, which began in the 1920s and has a nearly 100-year history, began in the 1920s. It is an industrial manufacturing technology that is widely used and well-established.
The following are some of the advantages of injection molding:
Injection molding has a number of significant advantages. It has the ability to be produced in large quantities while maintaining high precision and repeatability. When using plastic injection molding, you have the option of selecting from a variety of different materials to use. Through the use of additives, each material can have thousands of different variations, each of which results in a different set of characteristics.
Injection molding is capable of producing not only large quantities of product, but also intricate details in small quantities. As a result of the process's repeatability, it is very simple to meet the specifications of injection-molded parts. When it comes to manufacturing stronger parts, injection molding makes it extremely simple. In fact, fillers can be used in the injection mold during the injection molding procedure.
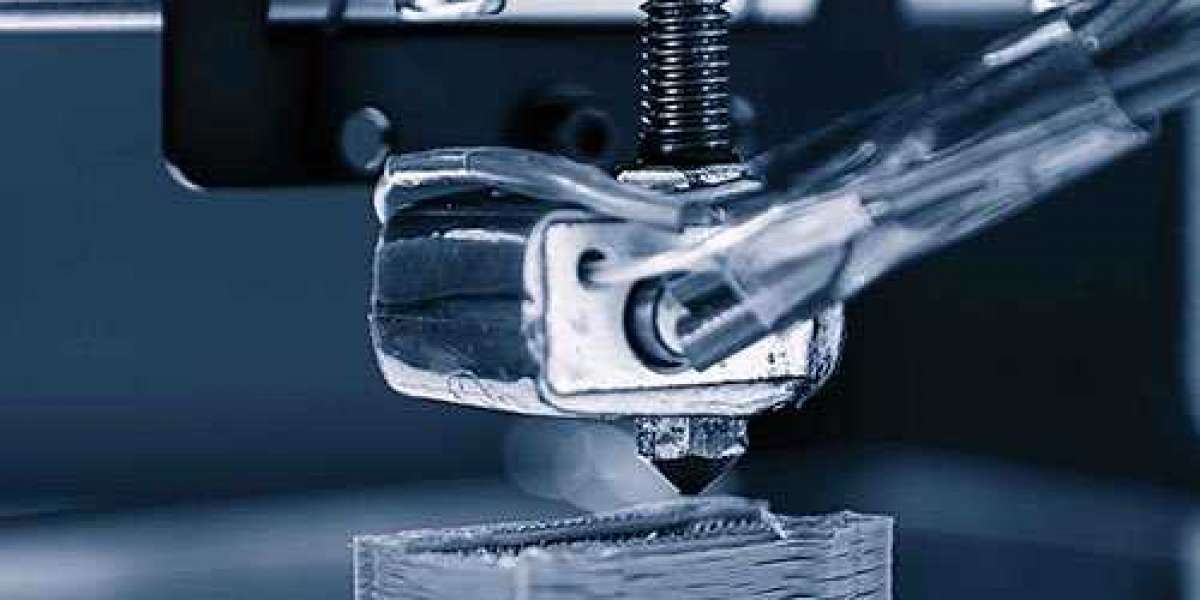
What Exactly Is 3D Printing?
A rapid prototyping technology based on digital model files, 3D printing uses powder metal / plastic and other adhesive materials to construct objects by layer printing, and is used to create objects in a short period of time. Using a 3D printer, you can create parts without the need to make a mold first. You only require a 3D printing model file, and there are numerous 3D printing technologies and materials available on the market to choose from.
The advantages of 3D printing:
First and foremost, 3D printing is an excellent tool for product iteration. Rapid prototyping has long been associated with 3D printing, and this has been the case for quite some time. Due to the fact that it has also evolved into a reliable manufacturing technology, this is no longer true. However, one of the most significant advantages provided by this manufacturing technology is the ability to prototype quickly and easily. In the case of 3D printing, you can print the project for testing, then use the 3D printing modeling software to make all of the necessary modifications, and then print the project again to ensure that the modifications were successful. The adaptability of this process will not only save you time and money, but it will also allow you to improve the design of your product as a result.
The use of 3D printing also helps to reduce waste of raw materials. When compared to traditional CNC processing methods, 3D printing can only use the amount of materials required for the entire project, reducing the amount of waste generated and the overall cost of production. You can also improve supply chain management by using 3D printing to avoid the need for additional inventory and the associated storage costs.
Injection Molding vs. 3D Printing: What Is the Difference? Injection Molding vs. 3D Printing: What Is the Difference?
1. Manufacturing mode
As long as injection molds are used in the injection molding process, it is possible to produce standardized products in large quantities at a low cost.
As a result, injection molding remains the most cost-effective method of producing traditional mass and large-scale quantities.
Traditional tools, fixtures, machine tools, and molds are not required when using a 3D printer because it does not require them. It has the ability to transform any shape on the computer screen into a physical model in an automated, quick, direct, and accurate manner. In part because of the characteristics of 3D printers, which are very different from traditional injection molding processes, the more complex the nonsolid object, the faster the processing speed, and the more the cost of raw materials is saved, the 3D printer is particularly suited for the production of personalized and diversified products.
2. Manufacturing Costs and Fees
Because of the wide availability of raw materials for injection molding, the characteristics of large-scale, rapid standardized production are also conducive to lowering the cost of a single product. In addition, the characteristics of large-scale, rapid standardized production are conducive to lowering the cost of a single product. Accordingly, when it comes to manufacturing costs, the cost of injection molding technology is significantly less expensive than the cost of 3D printing technology.
However, in industrial manufacturing, the real cost-saving link is in the modification of the prototype, which only necessitates the modification of the CAD model and does not necessitate the incurring of any manufacturing costs.
Mold tool modification costs are relatively low in injection molding if the prototype is a steel mold; however, if the mold tool is made of aluminum alloy, the cost will be significantly more expensive. This is also one of the reasons why many businesses or individuals involved in mold design will opt for a creative 3D printer for mold design and printing rather than traditional methods.
3. Application Fields
At the moment, the injection molding process is capable of achieving mass production of items with uniform shapes, making it particularly well suited for the mass production of standardized products.
All that is required for 3D printing are 3D images to be entered into the control terminal, which can then print the raw materials into physical models, and even directly manufacture parts or molds, thereby significantly shortening the product development cycle.3D printers for 3D production have become increasingly popular in a variety of fields, including maker, architectural design, mold model design, and others.